Javascript data types with examples
In this chapter, you will learn about javascript data types with examples. Let’s look at the fundamental concept of variables. Basically variables are a fundamental concept of all programming languages. Variable is like a storage box in which we can store a value in order to use it whenever we need in functions. Let’s see what are the different data types are available in javascript.
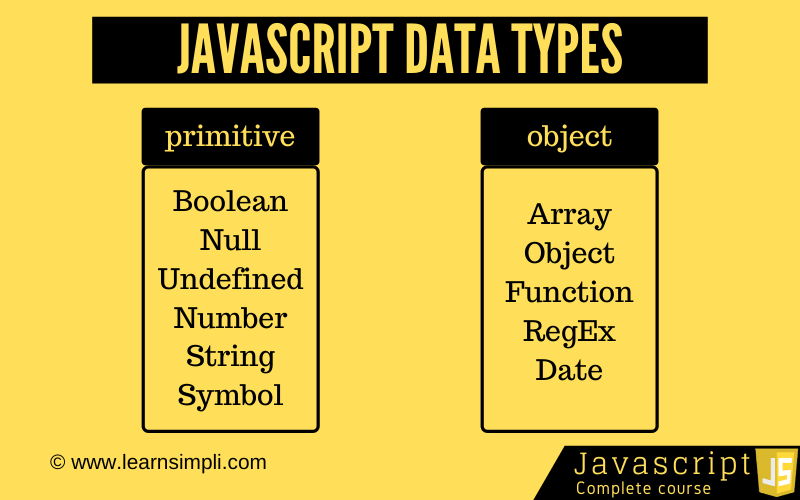
Javascript data types can be categorised into 2 categories
- Primitives values
- Non Primitives values
Primitives values:
There are 7 different data types that are primitives in the latest ECMAScript standard and they are
- Number: A data type represents floating-point numbers, for decimals and integers
- String: A data type represents a sequence of characters used for text.
- Boolean: A data type represents true or false
- Undefined: A data type variable that does not have a value yet
- Null: A data type variable that notifies variable points to none
- BigInt: A data type represents large integers even beyond the safe integer limit for Numbers.
- Symbol: A Symbol is a unique and immutable primitive value
Non Primitives values:
All objects such as functions, arrays and structured JSON.
Now let’s create Number data types:
const x = 1; const y = 2.5; const z = 2.5 + 3.5; console.log(x); console.log(y); console.log(z); // output // 1 // 2.5 // 6
Now let’s create String data types:
const employeeName = 'Mickel'; const lastName = 'Clark'; const department = 'IT'; console.log(employeeName); console.log(lastName); console.log(department); // output // Mickel // Clark // IT
Now let’s create Boolean data types:
const isAdmin = new Boolean(true);
const isSubscriber = new Boolean('true');
const isCustomer = new Boolean('false');
const isBuyer = new Boolean('true');
const isActive = true;
console.info(isAdmin);
console.info(isSubscriber);
console.info(isCustomer);
console.info(isBuyer);
console.info(isActive);
// output
// Boolean {true}
// Boolean {true}
// Boolean {true}
// Boolean {true}
// true
const isAdmin = new Boolean();
const isSubscriber = new Boolean(0);
const isCustomer = new Boolean(null);
const isBuyer = new Boolean('');
const isActive = true;
console.info(isAdmin);
console.info(isSubscriber);
console.info(isCustomer);
console.info(isBuyer);
console.info(isActive);
// output
// Boolean {false}
// Boolean {false}
// Boolean {false}
// Boolean {false}
// true
Now let’s create Undefined data types:
var employeeName; var employeeLastName; let employeeDepartment; console.log(employeeName); console.log(employeeLastName); console.log(employeeDepartment); // output // undefined // undefined // undefined
Now let’s create Null data types:
var employeeName = null; var employeeLastName = null; let employeeDepartment = null; console.log(employeeName); console.log(employeeLastName); console.log(employeeDepartment); // output // null // null // null
Dynamic typing:
One thing you might have noticed that we are using the var or let for creating the strings, numbers and null. Its because javascript is a loosely typed language. Let’s see the below examples
let employeeName = 'John'; console.log(employeeName); employeeName = 'Mickel'; console.log(employeeName); employeeName = 'Stark'; console.log(employeeName); // output // John // Mickel // Stark
2 thoughts on “Javascript data types with examples”
Comments are closed.